Over 90% of all Cyber-Attacks Involve Phishing – Tips to Stop Phishing Attacks
Phishing Accounts for Over 90% of Cyber-Attacks – Learn How to Stop Them
Among the billions of e-mails transmitted each day around the world, a significant and growing portion consists of e-mail attacks aimed at breaching an organization’s defenses to conduct criminal activity. This includes e-mail attacks in the form of phishing schemes designed to give the hackers control of or access to important corporate information or processes. Recently, many of these phishing attacks leverage ransomware which freezes a company’s IT system in an attempt to generate ransom payments to the attackers. This type of attack has been massively successful with over 3.4 billion fake e-mails every day containing some type of phishing attack.
What is Business E-mail Compromise?
Phishing attacks may aim at “business email compromise;” which is specifically a crime that targets businesses that send wire transfers, often to foreign suppliers, with the goal of fraudulently directing payments from the company whose defenses they have breached to accounts they control. BEC is a growing phenomenon, with victim losses increasing by over 100% last year.
What is a Ransomware Attack?
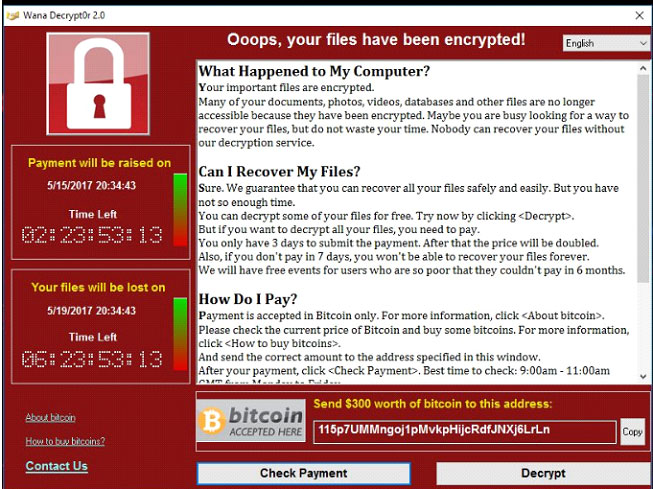
Ransomware attacks on the other hand typically do not aspire to the level of social engineering often involved in “spear-phishing” attacks. This is when a hijacked e-mail is often used to communicate with lower-level employees in an organization (as the criminal’s spoof or directly control the e-mail of higher-level executives of a firm) to siphon funds out of the company fraudulently. Instead, ransomware attacks use control of elements of a company’s IT network to lock down the company’s vital data via sophisticated encryption methods. Victims of such attacks are given a choice between paying the attackers ransom to, hopefully, unfreeze their data or losing the ability to access it.
Either type of attack can cause severe damage, whether by draining significant sums of money or by necessitating payment of a ransom or the exertion of significant time, effort, and expense to replicate the data or replace the systems that have been infected. With the scope or remote work increasing substantially in the wake of the novel coronavirus, it has become more important than ever to do everything possible to defend against malicious e-mails designed to gain control over or lock down a company’s IT system.
Defending Against Phishing Attacks with a 3-Pronged Approach
Defending against malicious phishing attacks that target e-mail vulnerabilities calls for a three-prong approach. The initial layer of defense typically consists of anti-virus software or e-mail security protocols that bar unauthorized e-mails from making it through an organization’s network. This weeds out many spammers or senders on reputation block lists (RBLs), suspicious IP addresses, identified malware, and the like.
The next layer of defense usually entails the use of advanced e-mail protection apps using artificial intelligence (AI) to sniff out e-mails from domains with low reputation scores, mismatched URLs, malicious links embedded within e-mails, and other such threats. This type of software can utilize machine learning to improve its understanding of phishing attacks to help identify and quarantine those that penetrate the initial layer of defense.
Finally, to help protect against the most sophisticated phishing attacks such as domain spoofing, clone phishing, corporate account takeover, brand impersonation, etc. staff training is essential. While these attacks are generally so complex that a company’s employees are unlikely to be able to identify all of them, a basic level of training should enable your staff to repel at least some of them.
When staff awareness is combined with effective anti-virus tools and proper email provisioning, or hardening, protocols, an organization can be confident that they are taking the steps necessary to defend themselves from malicious e-mail attacks.
Phishing Attacks Have Increased with COVID-19 and Remote Work
With the increase in remote work caused by the Coronavirus, it is clear that cybercriminals will devote extra effort to launching e-mail attacks designed to gain valuable information that can compromise an organization’s vital data assets. Their efforts are aided by the usage of SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) to send and receive an e-mail by many small and medium-sized businesses. This 30-year-old protocol leaves e-mail communications unsecured and thus vulnerable to attack.

Whatever e-mail system an organization uses, taking steps to defend against any vulnerabilities it presents is essential given the increasing sophistication of phishing attacks these days. Such steps include conducting training sessions and sending out security notices specifying e-mail best practices, upgrading to more secure e-mail systems, and acquiring cybersecurity software for defense against such threats.
Simple Ways to Prevent Ransomware Attacks by Hardening Your System
Ransomware attacks have posed a growing threat to corporate IT systems in recent years. By gaining control over aspects of an organization’s IT system through phishing attacks, exploiting endpoint and other system vulnerabilities, social engineering or some combination of the three, attackers are able to lock down vital data and systems and demand a ransom to restore access. They often accomplish this by using illicitly obtained administrative privileges to deploy encryptors across an IT system using Windows batch files or other deployment tools.
Besides the comprehensive approach to deter phishing attacks described above, another step companies can take to deter and limit their exposure to ransomware attacks is to harden their IT system, including Outlook and other e-mail systems. Rigorously hardening your IT system by systematically optimizing system settings and reducing or eliminating vulnerabilities can substantially increase your organization’s ability to avoid falling prey to a ransomware attack.
IT system hardening includes establishing robust endpoint security controls and provisioning enforcement measures to restrict the ability of any ransomware attack to adversely affect a broad spectrum of systems within an organization’s IT environment. Such measures often include:
- SMB protocols and policy changes
- MS Office settings
- Settings on specific MS Office applications
- Eliminating vulnerabilities
- RDP policy changes
We’ll take a look at what you can do to bolster your system’s defense in each of these areas.
SMB protocols and policy changes
When a ransomware event occurs, a number of these attacks make use of Server Message Block (SMB) to communicate between systems. SMB is utilized in Windows operating systems for communication between Domain Controllers and File Servers and workstations. However, the type of communications allowed between these systems can be limited to workstation-to-workstation to help restrict the use of SMB during an attack.
Windows Firewall policy can be used during such an event to regulate allowed communications between endpoints within the system. Additionally, PowerShell or the Microsoft Security Guide can be used to disable SMB v1.
MS Office settings
There are a variety of settings you can use in Microsoft Office to help harden your system against ransomware attacks. To gauge your progress in this regard, you can view your Microsoft 365 Secure Score via a dashboard in the Microsoft 365 security center. Steps you can take to improve system security include:
Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Setting up multi-factor authentication is a powerful step for boosting security at your organization. Doing so keeps hackers from being able to access your system even if they know your password.
Set up dedicated administrator accounts
Administrator accounts for Office 365 or Microsoft 365 afford their users powerful privileges within the Microsoft operating environment. To reduce the chance that hackers can gain control of these accounts, provide users of such accounts with separate accounts to use for non-administrative functions. This serves to minimize the use of administrative accounts within the environment. Additionally, be sure to enable multi-factor authentication for administrative accounts.
Ramp up malware protection settings
Blocking attachment file types which are often accompanied by malware payloads helps increase the security of e-mail accounts.
Create mail flow rules to thwart ransomware attacks
Warning users or blocking file extensions associated with ransomware attacks by creating mail flow rules can help protect against these attacks propagating via e-mail. This can include simple warnings to users prior to opening Office file attachments that contain macros, which can be used to hide ransomware.
Turn off email auto-forwarding
To prevent hackers from using a mailbox they control to exfiltrate mail by setting up automatic email forwarding, you can configure a mail flow rule to make sure this can’t happen.
Utilize Office Message Encryption
Included in Microsoft 365 is Office Message Encryption. This tool enables you to send and receive encrypted e-mails inside and outside your organization. This helps make sure that only authorized recipients are able to see email messages.
Use ATP safe attachments to repel questionable attachments
Attachments are commonly shared between people within and outside an organization. In many cases, it is difficult to discern between malicious and trustworthy attachments. ATP Safe Attachment helps identify malicious attachments. It comes with Office 365 but is not enabled by default. You can engage it by setting up a new rule to use it.
Settings on specific MS Office applications
Many ransomware attacks attempt to infiltrate via Microsoft Office apps like Excel and Word. To defend against such attacks, Microsoft has added security features to Office 365 that help fight ransomware and other malware attacks.
These include:
- Ransomware detection and recovery: Detects ransomware attacks and notifies you via an email or other notification and helps you bring back your OneDrive to a point prior to the malware attack.
- Files Restore: This feature enables the restoration of an entire OneDrive to an earlier time benchmark anytime in the preceding 30 days.
- Link sharing protected by passwords: With this feature, you can set a password to guard shared files and folders.
Eliminating vulnerabilities
Along with minimizing the use of administrator accounts, another vulnerability to focus on is the use of credentials and tokens located on endpoints. Older Windows Operating Systems store cleartext passwords in memory in order to enable WDigest authentication. To ward against this vulnerability, disable WDigest if this is not the default setting.
Another vulnerability to protect against is to see if any applications are listed in “Allow” keys which would enable cleartext passwords to be stored in memory.
In some ransomware attacks, hidden network shares are used to link to endpoints throughout a system. To prevent this, you can prohibit access to default administrative or hidden shares on endpoints. This can be accomplished via registry modification, terminating a service, or use of the “Microsoft Security Guide” Group Policy template.
RDP policy changes
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) is often used by attackers to establish a remote connection to an environment, then move from the perimeter to the core of the system to deploy malware. Systems in which RDP is open to the internet face increased risk. If a hacker infiltrates a system via RDP, they can either steal data or lock it down via ransomware.
To gauge your organization’s vulnerability via RDP, you can scan its public IP addresses to see if any feature RDP protocols are accessible via the internet. To deter attackers, both RDS and SMB should not be accessible to/from the internet. In cases where external-facing RDP needs to be used for specific operations, the use of multi-factor authentication should be employed. Furthermore, controls should be established to limit the source IP addresses allowed to interact with systems that utilize such protocols.
Phishing and ransomware can severely damage your company’s IT assets. Taking steps to harden your system’s defenses against malicious attacks of this nature can improve your ability to repel and such attacks and limit any damage they may cause. The hardening steps outlined in this article are by no means exhaustive, but they can help you build a robust strategy to protect your system from being exploited by hackers.
Conclusion – Responding to Ransomware Attacks
Disconnect Your System: Take your system off of the corporate network immediately to avoid the spread of the infection to the rest of the network. Malware typically moves laterally from the infected system to higher-level systems to gain access to more valuable data. Identifying and disconnecting the infected device may prevent the spread of the malware.
Try Your Antivirus Software: Older versions of ransomware can often be removed simply by running your antivirus or anti-malware software.
Wipe Your Machine & Recover Your Data: Please back up your data either by using a separate hard drive that you periodically update with new files or simply through a cloud back-up system like OneDrive with ActiveSync, Dropbox or Box. By reinstalling the operating system and restoring files from your backups, you will be able to avoid the absolute, worst-case scenario.
To Learn More About How to Protect Yourself from Ransomware and Phishing Attacks Please Call Us – as Always We Are Happy to Help – 1 (888) 982-0678







