Implementing Vulnerability Management Programs is Still Challenging for Many Companies – Part 1
We’ve written considerably on Vulnerability Management, Vulnerability Assessments, and Patch Management because they are critical to preventing cyber attacks. I’ve provided links to several of the most-read blog posts we have written on the subject. In this blog post series, we’ll discuss the 2023 State of Vulnerability Management Report, a survey conducted by Cybersecurity Insiders and how organizations are handling the challenges of implementing vulnerability management best practices.
Assessing and Mitigating the Log4j Vulnerability – A Vulnerability Management Case Study
https://secureops.com/blog/log4j-vulnerability-management/
Developing a Risk-Based Vulnerability Management Program A Real-Life Case Study
https://secureops.com/blog/vulnerability-management-program/
ZeroLogon Illustrates Importance of Vulnerability Management
https://secureops.com/blog/zerologon-vulnerability/
What You Need to Know About Vulnerability Assessments – How Vulnerability Assessments Differ Across Providers
https://secureops.com/blog/effective-vulnerability-assessments/
As you can see from the multiple blog posts we’ve written on vulnerability assessments, vulnerability management, patching, and pen testing, we believe that a comprehensive risk-based vulnerability management program is still challenging for many organizations. The 2023 State of Vulnerability Management Report was released recently and is based on a comprehensive global survey of 421 cybersecurity professionals conducted in June 2023 to gain deep insight into the latest trends, key challenges, and vulnerability management solutions. The respondents range from technical executives to managers and IT security practitioners, representing a balanced cross-section of organizations of varying sizes across multiple industries.
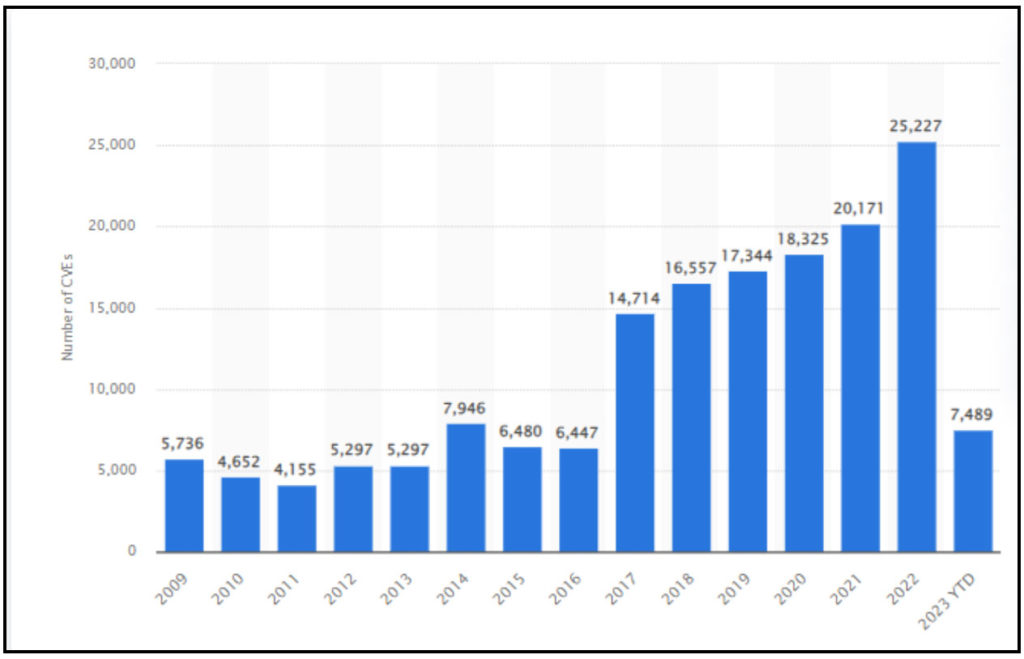
In 2022, internet users worldwide discovered over 25 thousand new common IT security vulnerabilities and exposures (CVEs), the highest reported annual figure to date. Between January and April 2023, this number amounted to 7,489. As you can see from the chart, the number of detected CVEs has significantly increased in the past decade.
The survey was conducted because we at SecureOps and most other security organizations understand that managing cybersecurity vulnerabilities still poses a substantial challenge for most organizations. Unresolved vulnerabilities expose systems to cyber threats, and the sheer magnitude of potential risks can hinder the effective prioritization of remediation tasks. Rapid technological advancements and the continuously expanding attack surfaces often outstrip organizations’ capacities to address emerging threats proactively.
Further, this survey was designed to shed light on current practices, obstacles, and perspectives in vulnerability management. By understanding how organizations tackle these challenges, the “2023 State of Vulnerability Management” report offers strategic insights and industry benchmarks.
Key Objectives for Vulnerability Management Programs
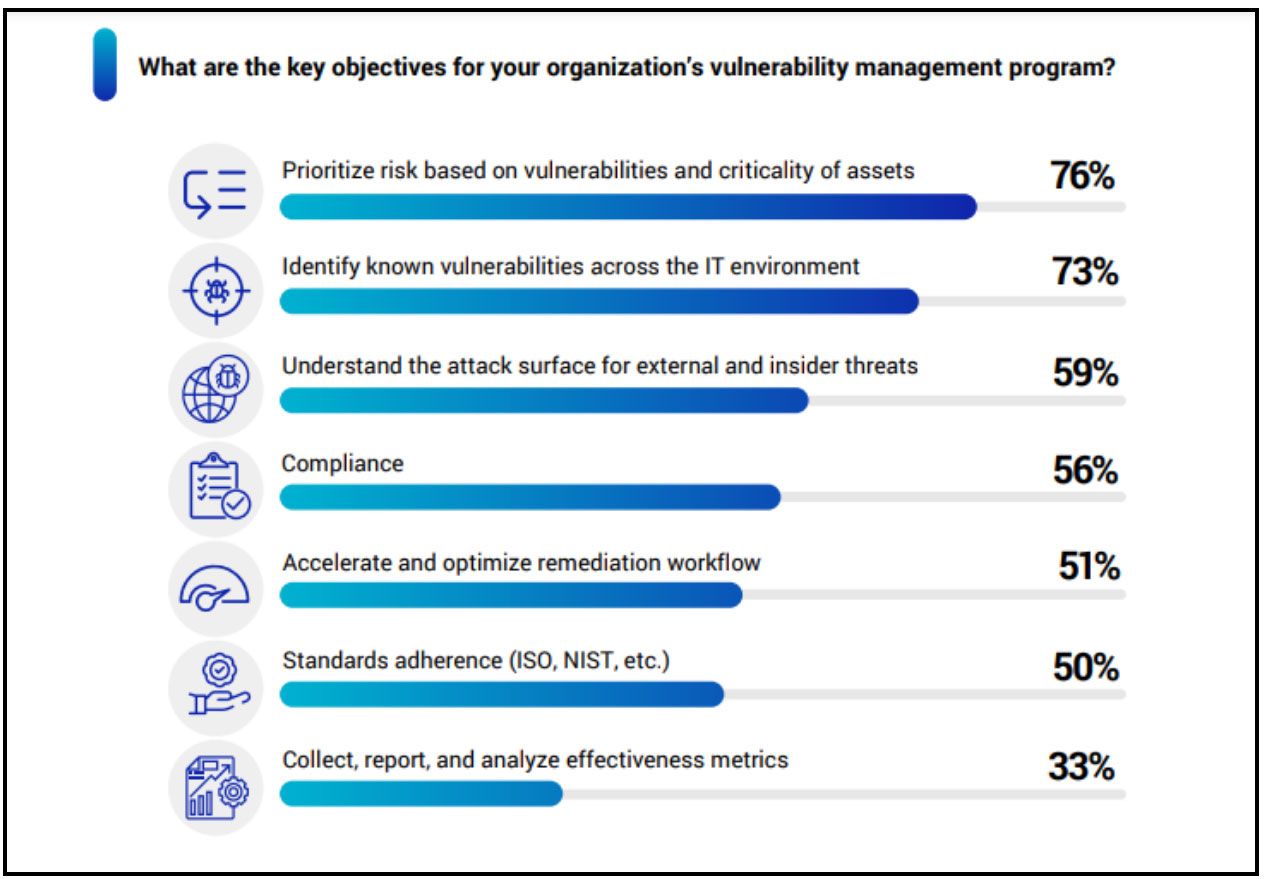
Key findings from the survey include:
- Real-World Impact: Nearly a quarter of the organizations surveyed (24%) reported experiencing a breach due to unaddressed vulnerabilities, revealing the real-world implications of neglected vulnerabilities.
Application security organization, Rezilion posted a June 8 blog that detailed the top seven vulnerabilities of the first half of 2023. What came out of the research was that it’s difficult to pinpoint which vulnerability to focus on first — much depends on the type of business, technology organization, and what the staff uses the applications for. But as a general rule, Rezilion said security teams should focus on the recent Apache Superset, Papercut, MOVEit, and ChatGPT vulnerabilities. The challenge is for security teams to prioritize which patches to focus on because of the more than 20,000 vulnerabilities reported each year; under 5% are actually exploited in the wild.
- Preventive Measures: While most organizations (85%) use network vulnerability scans, applying other preventive measures varies. Only 65% prioritize vulnerabilities based on risk. Several security reports showed that new vulnerabilities are increasingly used by cybercriminals—those reported in the past three years were used in 24% percent of exploitation attempts in 2022, compared to only 18% of attempts in 2021.
- Visibility and Detection: Half of the organizations (51%) have, at best, only a moderate level of visibility into vulnerabilities, and 26% detect over 100 new vulnerabilities every month. This underlines the sheer volume of potential risks organizations contend with, necessitating efficient vulnerability management strategies.
- Vulnerability Scanning and Patching Speed: While 35% of respondents employ continuous vulnerability scanning, there remains a considerable lag in patch deployment. Surprisingly, only 11% manage to deploy patches on the same day they become available, with a significant number of security teams (47%) taking more than a week to apply patches. This gap creates a significant risk window during which organizations remain susceptible to exploited vulnerabilities.
- Scope of Vulnerability Scanning: The survey results contrast what organizations currently scan and where they perceive the need for more comprehensive vulnerability management. Servers (91%) and desktops/laptops/endpoints (80%) are the most scanned assets. However, respondents expressed a need for improved vulnerability management in areas like IoT/OT devices (49%) and cloud assets (44%).
- Maturity of Approach: Approximately 70% of respondents classified their vulnerability management program as Level 3 or higher. This indicates their capability to analyze and prioritize vulnerabilities according to the specific IT environment risk (Level 3: 28%), conduct scanning and penetration testing (Level 4: 23%), and establish comprehensive vulnerability management programs (Level 5: 19%). Notably, only 19% of organizations have attained a high-level maturity in their vulnerability management program, indicating significant potential for industry-wide enhancement.
And thank goodness, only 1% of organizations in our survey indicated the absence of any program.
- Barriers to Improvement: Most organizations identified budget constraints (56%) and skill shortages (46%) as the most substantial barriers to improved vulnerability management, highlighting the growing need for innovative solutions and automation to facilitate greater efficiency among existing staff.
- Solution Priorities: In evaluating vulnerability management solutions, survey participants assigned the utmost importance to the accuracy of vulnerability detection (79%), closely followed by reporting and analytics capabilities (63%) and the cost of ownership (61%).
Network Vulnerability Scans (85%) and Penetration Testing (76%) are the most widely employed components, reflecting these techniques’ essential role in identifying vulnerabilities. Despite the high uptake of these methods, it’s concerning that more advanced and targeted measures like Adversary Simulation (21%) and Breach and Attack Simulation (34%) are less used.
Timely Scanning and Patching Using a Risk-Based Approach is Critical

Although the majority of respondents are conducting vulnerability scans continuously (35%), daily (10%), or weekly (26%), a surprising number of organizations are only scanning on a monthly (15%) or quarterly basis (11%), leaving long periods of potential exposure to cyber threats.
In addition, extending vulnerability scanning across all facets of the IT environment is of utmost importance, as cybercriminals possess the capability and intent to exploit vulnerabilities within any network infrastructure segment.
It is encouraging to observe a substantial proportion of organizations conducting scans on servers (91%), desktops/laptops/endpoints (80%), and network infrastructure devices (76%). However, a noteworthy number of respondents overlook susceptible areas such as IoT/OT devices (24%), middleware (32%), and data assets (38%). This raises concerns, as these components can serve as crucial ingress points for malicious actors.
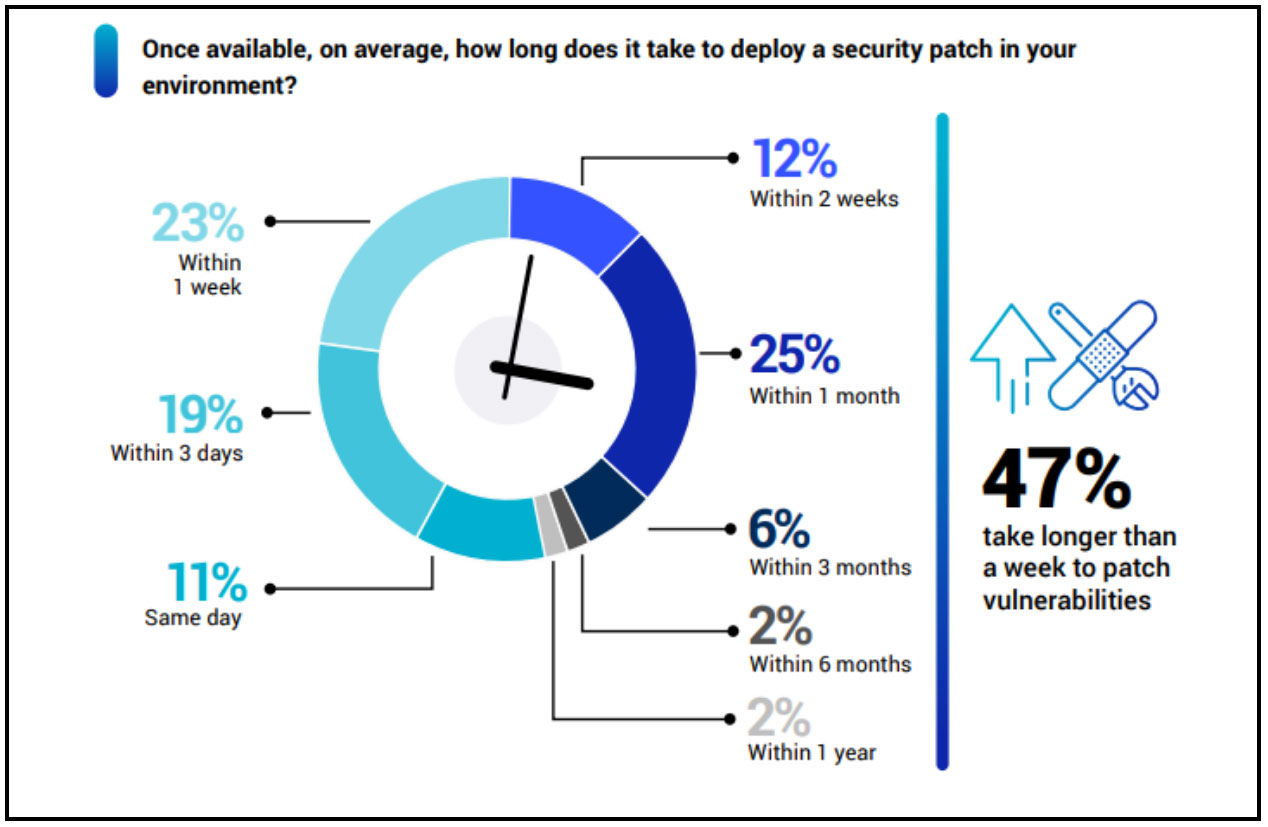
Only 11% of organizations successfully deploy patches on the same day they become available. Within 3 days, 19% of organizations manage to patch, while 23% do so within a week. Notably, 47% take more than a week to complete the patching process. Of particular concern is the fact that a combined 10% of organizations require more than a month to patch known vulnerabilities. Delays in patch management significantly elevate an organization’s risk of a security breach.
Vulnerability Management as a Service (VMaaS) vendors identify, prioritize, and respond to vulnerability exposure on behalf of the organization. It helps fill in the gaps left by talent and resource shortages, letting organizations take advantage of the vendor’s security staff to manage the organization’s vulnerability management process.
Conclusion – 6 Vulnerability Management Priorities
Vulnerability management is a challenging task as practically anything can turn into a system’s vulnerability. This includes running outdated software versions, unpatched operating systems, and even users and employees falling prey to email phishing schemes and targeted attacks.
Continuously performing vulnerability management is crucial to ensure that all systems stay up-to-date and that each new vulnerability is promptly discovered. However, this process demands tremendous energy and time from IT staff, which can quickly become overwhelming for organizations, particularly small businesses.
One additional challenge companies face is coordinating and planning the implementation of fixes to minimize downtime and service interruptions. Engineering teams must conduct practice runs of vulnerability patching in non-production environments beforehand to ensure the smooth application of patches in production environments. Although time-consuming, this meticulous process helps prevent any potential issues.
With all of that said, here are 6 priorities that organizations can focus on to eliminate the vast majority of vulnerabilities:
- Patch Management: Vulnerability management often requires effective patch management, which can be complicated due to the need to test patches in various environments before deployment. Companies may have difficulty balancing the need for security with the potential for patch-related disruptions.
- Scale and Scope: For large and complex organizations, the scale and scope of vulnerability management can be overwhelming. Identifying, tracking, and remediating vulnerabilities across a vast network of systems and applications can be a daunting task.
- Vendor and Third-Party Risks: Companies may struggle with managing vulnerabilities in third-party software and services, as they often have limited control over these components of their IT infrastructure.
- Resource Constraints: Many organizations struggle with limited resources regarding budget and personnel. Implementing a comprehensive vulnerability management program often requires investments in tools, staff training, and dedicated time, which can strain already stretched resources.
- Complexity of IT Environments: Modern IT environments are increasingly complex, with a mix of on-premises, cloud-based, and hybrid systems. Managing vulnerabilities across such diverse environments can be daunting, especially if the company lacks a clear inventory of assets.
- Lack of Awareness: Some organizations may not fully understand the importance of vulnerability management or underestimate potential risks. This can lead to a lack of motivation to invest in such a program.
Ok, we’ve established how organizations handle all the challenges of vulnerability management, where they are in terms of vulnerability management maturity, and where organizations should focus their time and energy to shift their vulnerability management to manage risk cost effectively. In part 2 of this blog post series, we will review several case studies to understand real-life successes and failures of vulnerability management.
To Learn More About Vulnerability Management Services or If You Have Been Attacked, Please Call Us – as Always, We Are Happy to Help – 1 (888) 982-0678.
You Can Also Fill Out Our Contact Us Form Here to Talk with a Security Specialist – https://secureops.com/contact-us/






