The Benefits of Building a Zero-Trust Network
In a previous blog post titled, The 5 Steps to Building a Zero Trust Network; we suggested “the Zero Trust model is the response to the realization that the perimeter security approach hasn’t been effective because many data breaches happened because attackers, once they got past the corporate firewalls, were able to move through internal systems without the risk of being uncovered and stopped.” In a second blog post on Zero Trust titled, organizations Struggle Implementing Compliance Requirements Including NIST & Zero Trust Mandates; which said “President Biden issued an executive order (EO) aimed at improving America’s cybersecurity posture – a move primarily in response to the SolarWinds breach among other recent high-profile software supply chain attacks. The Executive Order said the following:
- It instructed federal departments and agencies to implement multi-factor authentication and encryption for classified systems within 180 days
- It provided the Committee on National Security Systems (CNSS) 90 days to come up with a cybersecurity framework for systems in the commercial cloud
- It provided the head of each executive department or agency 60 days to update plans to prioritize the adoption of cloud technology and a zero-trust architecture
Defining Zero Trust and Microsegmentation
Let’s take a step back from those two blog posts and precisely define Zero Trust and Microsegmentation and then discuss the benefits. Zero Trust is a network security model that operates on the basis of strict identity verification. This framework enforces the principle that only authenticated and authorized users and devices are granted access to applications and data without exception. Its core focus is on safeguarding sensitive data, including personally identifiable information (PII), protected health information (PHI), payment card information (PCI), and intellectual property (IP), all of which hold significant value to potential attackers.
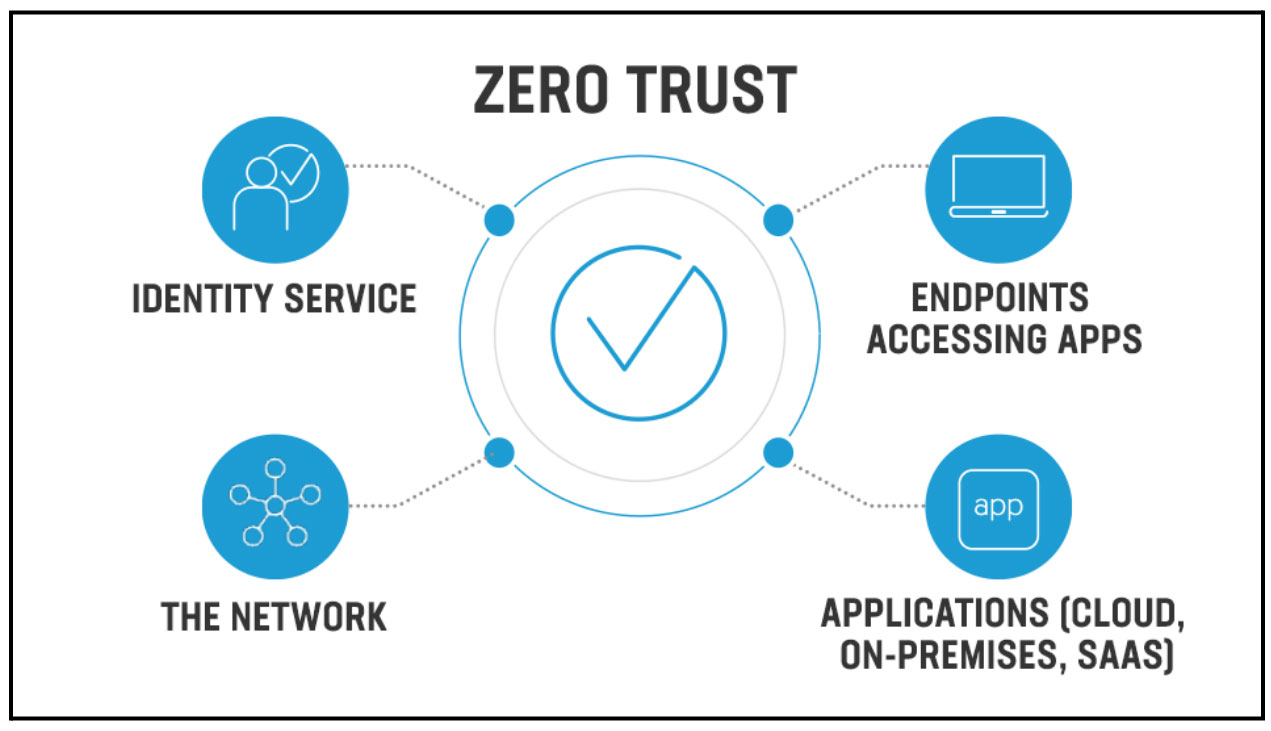
The Zero Trust model emerged as a response to the realization that traditional perimeter security approaches have proven inadequate. Many data breaches occurred because attackers could move freely within internal systems without detection or prevention once they breached corporate firewalls. Moreover, the concept of a clear-cut perimeter has become blurred as applications and data reside both on-premises and in the cloud and users access them through a variety of evolving technologies.
Now that we understand the underlying rationale let’s delve into the fundamental principles that can help protect your data within the Zero Trust model before delving into the details of its implementation:
- Identify sensitive data: Determine where sensitive data resides within your systems and who has access to it. This assessment enables you to gain awareness of the data’s location and potential vulnerabilities.
- Limit access: Once you identify who has access to PII and other sensitive data, consider implementing access limitations. By restricting access to only those who truly require it, you can reduce the risk of unauthorized exposure.
- Detect threats: Monitoring all activities related to data access is vital. This includes tracking activity within the active directory, file and share access, and network perimeter telemetry. By diligently monitoring these areas, you can identify potential threats and take proactive measures to mitigate them.
- Establish a baseline of network activity: Creating a baseline of normal network activity allows you to evaluate anomalies effectively. While not all abnormalities are incidents, attacks often result in noticeable deviations from the established baseline, indicating a potential security breach.
- Apply analytics: Leveraging advanced analytics can significantly enhance threat detection. Analytical tools have evolved to a point where they can swiftly and accurately identify attacks, surpassing the effectiveness of manual log review. Integrating analytics into your security infrastructure can expedite incident response and strengthen overall protection.
By adhering to these five basic principles within the Zero Trust model, organizations can fortify their data security measures and establish a robust defense against evolving threats.
The Benefits of Zero Trust and Microsegmentation
With the definition clarified and the pieces of Zero Trust and Microsegmentation clarified let’s explore the numerous benefits that Zero Trust and Microsegmentation offer and how they can enhance organizations’ overall security posture.
- Enhanced Data Protection:
Zero Trust and Microsegmentation provide organizations with a granular approach to data protection. Organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access by implementing Zero Trust principles, such as identity verification and strict access controls. Microsegmentation complements Zero Trust by dividing the network into isolated segments, ensuring that the remaining network remains secure even if one segment is compromised.
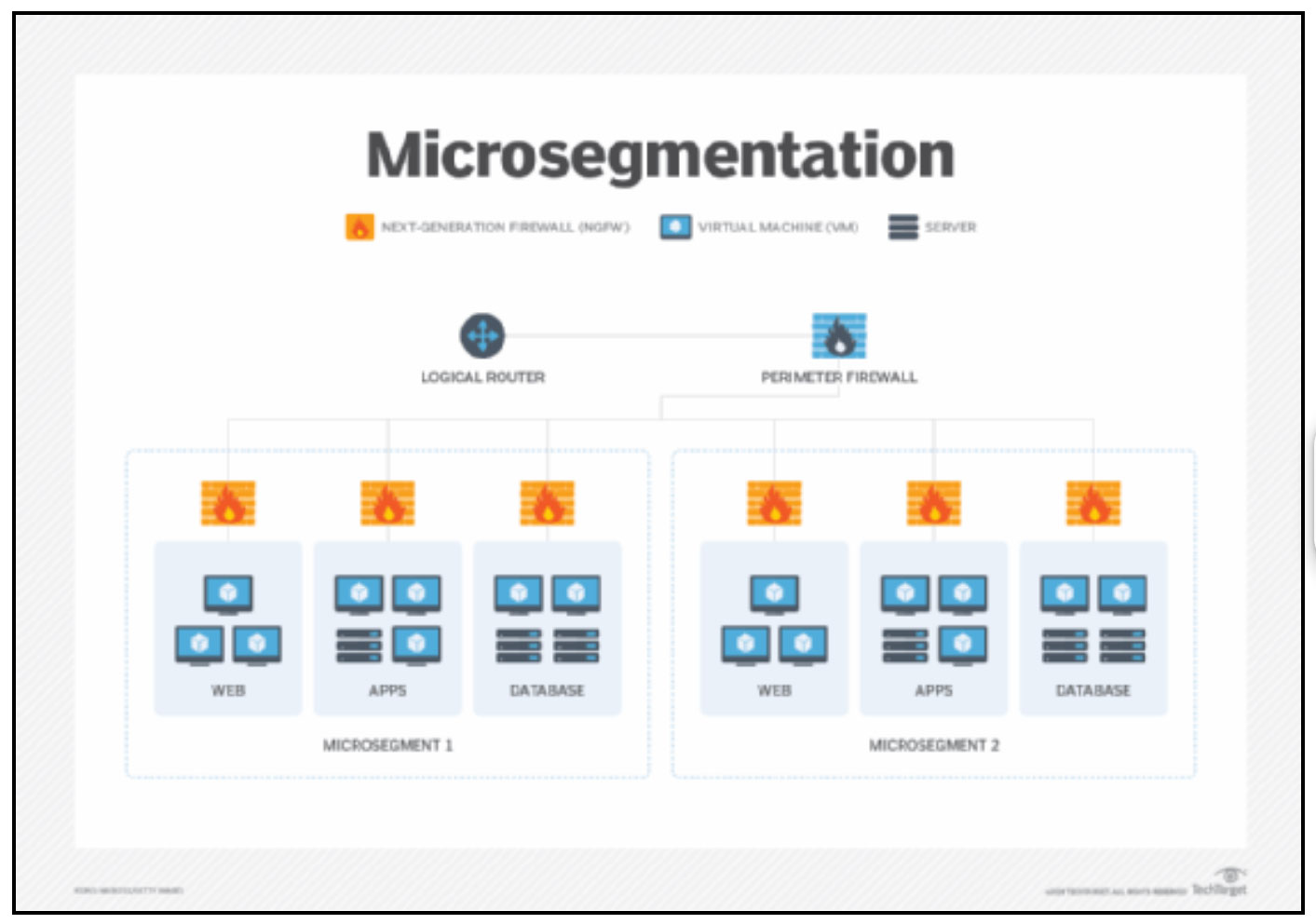
- Increased Visibility and Control:
Zero Trust and Microsegmentation empower organizations with enhanced visibility and control over their network traffic. By implementing Zero Trust policies, organizations gain a comprehensive understanding of all user activities and network flows, allowing them to identify potential security gaps or anomalous behavior more effectively. Microsegmentation further strengthens this control by enabling organizations to define and enforce strict traffic rules within each segment, limiting lateral movement of threats.
- Minimized Attack Surface:
Zero Trust and Microsegmentation significantly reduce an organization’s attack surface. With Zero Trust, the default stance is to deny access, requiring users and devices to prove their identity and authorization before accessing resources. This approach ensures that only authorized entities have access to critical assets, limiting the exposure to potential attackers. Microsegmentation takes this a step further by isolating critical assets and applications into separate segments, minimizing the potential impact of a breach.
- Agility and Scalability:
Contrary to the misconception that strong security measures hinder agility and scalability, Zero Trust and Microsegmentation can actually enhance these aspects. By adopting Zero Trust principles, organizations can establish secure connections between users, devices, and resources regardless of their location, facilitating remote work and enabling rapid deployment of new applications. Microsegmentation provides organizations with the flexibility to adapt their security policies to changing business requirements, allowing them to scale their security measures efficiently.
- Compliance and Regulatory Alignment:
For organizations operating in regulated industries, such as finance or healthcare, complying with industry-specific regulations and standards is essential. Zero Trust and Microsegmentation help organizations meet these compliance requirements effectively. The granular access controls, robust authentication mechanisms, and comprehensive visibility offered by these security approaches align well with the stringent regulations in many industries, ensuring organizations can meet their compliance obligations.
Conclusion
Zero Trust and Microsegmentation are two powerful security strategies that offer numerous benefits to organizations looking to enhance their cybersecurity posture. By implementing these approaches, organizations can achieve enhanced data protection, increased visibility and control, minimized attack surfaces, improved agility and scalability, and regulatory compliance. Embracing Zero Trust and Microsegmentation strengthens an organization’s security defenses and provides peace of mind in an ever-evolving threat landscape.
To Learn More About How to Implement a Zero Trust Network or If You Have Experienced a Breach Please Call Us – as Always, We Are Happy to Help – 1 (888) 982-0678.
You Can Also Fill Out Our Contact Us Form Here to Talk with a Security Specialist – https://secureops.com/contact-us/







