The Solution to Overcoming Firewall Management Challenges
Unleashing the Power: Next-Generation Firewalls vs. Traditional Firewalls
As we all know, cyber threats are growing increasingly sophisticated in our modern, globally connected world. In order to safeguard our digital assets, we must prioritize our cybersecurity measures. Firewalls have traditionally been relied upon as a first-line of defense against unauthorized access and malicious activity. However, as technology evolves, so do the threats we face. This has spurred the development of next-generation firewalls (NGFWs), which offer superior capabilities compared to their predecessors. In this article, we will provide an overview of the benefits of NGFWs and how they surpass traditional firewall technology.
Previously, we wrote two blog posts on the benefits of a SIEM and a traditional firewall on improving security defense and another discussing the challenges; links to both posts are listed below.
The Benefits of Using a SIEM to Improve IT Security
https://secureops.com/blog/blog-what-is-a-siem/
Overcoming the Challenges of Firewall and SIEM Management
https://secureops.com/blog/siem-and-firewall-management/
What is the Difference Between a SIEM and a Firewall?
Let’s start with the basics between a SIEM and a Firewall. In its most basic form, a firewall is meant to block inbound and outbound “connections,” a connection being a traffic flow identifiable by a “tuple,” or three specific parameters: the source IP address, destination IP address, and destination port. By blocking connections, a firewall prevents things that shouldn’t occur.
To be clear, a firewall provides your first line of perimeter defense. The firewall allows or denies traffic in or out, while a SIEM analyzes log files. Now let’s dig into the specifics.
What is a SIEM
- Focus: SIEM systems primarily collect, analyze, and correlate security events and logs from various sources within a network or system.
- Function: SIEM solutions provide real-time monitoring, threat detection, incident response, and compliance reporting by centralizing and analyzing security event data.
- Data Collection: SIEMs gather logs and events from various sources such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS), antivirus software, and more, enabling comprehensive visibility across the network.
- Analysis Capabilities: SIEM platforms leverage advanced analytics and machine learning techniques to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and uncover potential security threats or breaches.
- Incident Response: SIEM systems play a crucial role in incident response by providing alerts, automating response workflows, and facilitating forensic investigations.
What is a Firewall?
- Focus: Firewalls are network security devices designed to control and monitor traffic flow between networks or systems, enforcing security policies and filtering network packets.
- Function: Firewalls act as a barrier between internal and external networks, inspecting and filtering incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predefined rules or policies.
- Traffic Control: Firewalls make decisions about allowing or blocking specific network connections or packets based on factors like source IP, destination IP, ports, protocols, and application-specific rules.
- Network Protection: Firewalls provide protection against unauthorized access, external threats, and network-based attacks by applying access controls and filtering mechanisms.
- Perimeter Defense: Firewalls are commonly deployed at the network perimeter to protect internal resources from unauthorized external access, acting as a first line of defense.
The Bottom Line – SIEM systems provide centralized security event management, threat detection, and incident response capabilities, while firewalls primarily control network traffic and enforce security policies at the network level. While both SIEMs and firewalls contribute to overall network security, their primary focuses and functionalities differ.
What is a Next-Generation Firewall?
A next-generation firewall is within the third generation of firewall technology, designed to address advanced security threats at the application level through intelligent, context-aware security features. An NGFW combines traditional firewall capabilities like packet filtering and stateful inspection with others to make better decisions about what traffic to allow.
A next-generation firewall can filter packets based on applications and inspect the data contained in packets (rather than just their IP headers). Let’s get into the specifics now.
- Advanced Threat Detection and Prevention:
One of the key differentiators of next-generation firewalls is their ability to provide advanced threat detection and prevention mechanisms. NGFWs go beyond simple packet filtering by incorporating deep packet inspection (DPI) techniques. NGFWs can detect and block sophisticated threats, such as malware, viruses, and application-layer attacks by analyzing the entire packet payload. This proactive approach allows organizations to stay one step ahead of cybercriminals and mitigate risks effectively.
- Application Awareness and Control:
Traditional firewalls primarily focus on port and protocol-based filtering, which may not provide sufficient granularity to manage modern network traffic. Next-generation firewalls, on the other hand, possess deep insight into applications traversing the network. They can identify specific applications, including those using non-standard ports or encrypted traffic, and enforce granular policies based on the application, user, and content. This level of application awareness enables organizations to enhance network performance, prioritize critical applications, and enforce security policies tailored to each application’s requirements.
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) Integration:
While traditional firewalls can block unauthorized access attempts, they often lack the ability to detect and prevent sophisticated intrusion attempts. NGFWs integrate intrusion prevention systems, which combine signature-based and behavior-based techniques to identify and block network attacks in real-time. By leveraging threat intelligence databases and continuous monitoring, NGFWs can proactively protect against known and emerging threats, minimizing the risk of successful network breaches.
- User Identity Awareness:
Another significant advantage of next-generation firewalls is their ability to identify and enforce policies based on individual user identities. By integrating with authentication systems such as Active Directory or LDAP, NGFWs can associate network activity with specific users or groups. This level of granular control ensures that access privileges are tailored to individual needs, reducing the risk of unauthorized access or insider threats. User identity awareness also facilitates enhanced visibility into user behavior, simplifies auditing and compliance processes, and enables more effective incident response.
- Secure Remote Access:
With the rise of remote work and the increased adoption of cloud services, secure remote access has become a critical requirement for organizations. Next-generation firewalls offer built-in virtual private network (VPN) capabilities, allowing secure access to internal resources from remote locations. These firewalls can provide secure connectivity, enforce access policies, and inspect encrypted traffic to detect any potential threats. By consolidating remote access and network security into a single solution, NGFWs simplify network management and reduce complexity.
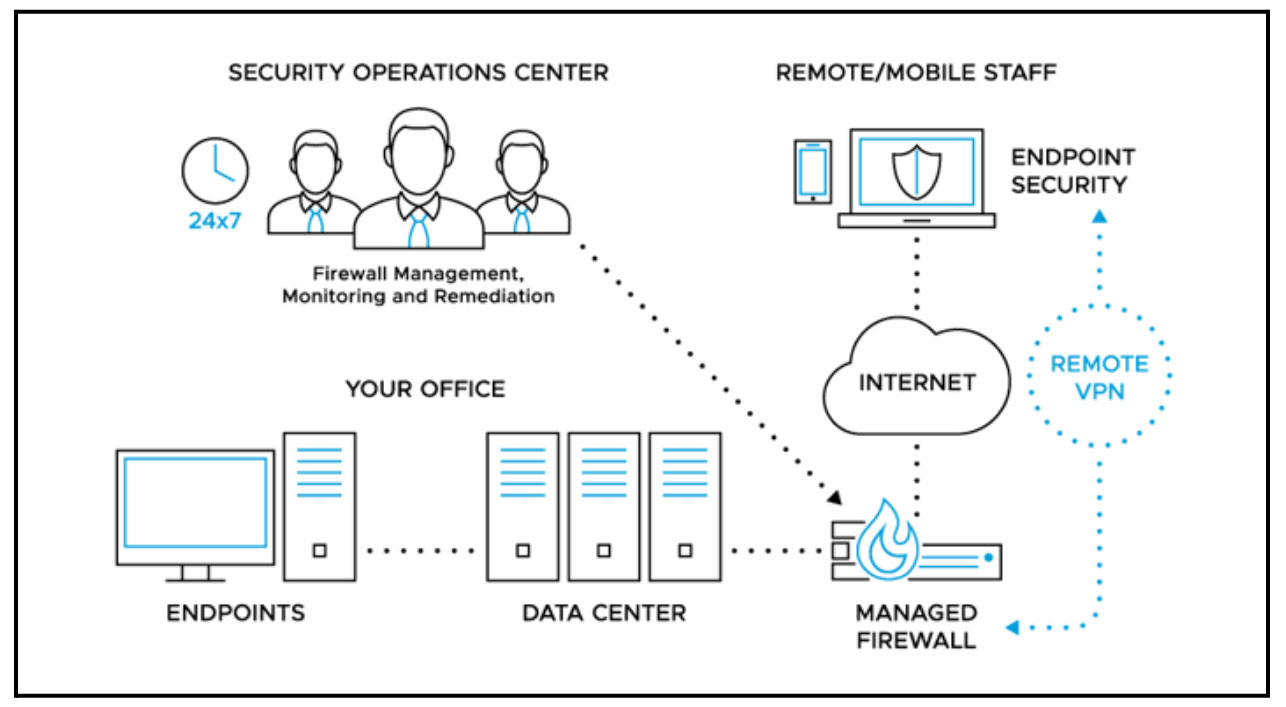
A Managed Firewall Provides Countless Benefits
A firewall is crucial for network security, but its efficacy depends on proper configuration and management. Mishandling a firewall can be more detrimental than no firewall at all, providing a false sense of security. Firewalls can be hardware or software-based and have specialties like Packet filters, Stateful firewalls, Application layer firewalls, and Next Generation Firewalls (NGFW).
Effective firewall security requires well-designed rules. Making rules too general or not explicitly defining the traffic type can increase the likelihood of malicious traffic slipping through. Additionally, failing to block internal protocols or not restricting access to certain protocols, like SSH, could lead to the unwanted exposure of sensitive data. Overall, firewalls can be powerful tools for combating cyber threats, but their potential is only realized through properly designed and enforced firewall rules.
To ensure optimal cybersecurity, it’s critical that firewalls are not merely set up and left to run independently. Regular monitoring and updates must be part of an organization’s cybersecurity strategy. Failure to monitor and manage a firewall can lead to several issues, including missed updates, which may render a firewall vulnerable to exploitation or incapable of monitoring network traffic. Overlooked security events can persist unnoticed in firewall-generated logs, leaving an organization unaware of ongoing cyberattacks. Additionally, as businesses grow, so do their security requirements. Outdated firewall solutions may be unable to keep up with traffic volumes or monitor all of an organization’s network traffic effectively.
Managed SIEM’s and Firewall’s offer businesses crucial core services, such as security monitoring and incident response. They also offer a range of other complementary services, such as monthly security reports, installing patches and updates, managing compliance, and maintaining the SIEM configuration and asset inventory functions. By partnering with a Managed Security Service Provider (MSSP), organizations can experience top-notch cybersecurity without the need to manage the solutions in-house. This allows businesses to access the right tools, expertise, and resources for first-class cybersecurity protections, including high-quality, curated alerts.
Conclusion
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the need for robust and advanced network security solutions is more critical than ever. Next-generation firewalls provide a significant leap forward compared to traditional firewalls, offering advanced threat detection and prevention, application awareness and control, integration with intrusion prevention systems, user identity awareness, and secure remote access capabilities. By embracing the benefits of NGFWs, organizations can strengthen their security posture, enhance network performance, and safeguard their valuable digital assets against a wide range of cyber threats.
To Learn More About Managed SIEM and Firewall Services or If You Have Been Attacked Please Call Us – as Always, We Are Happy to Help – 1 (888) 982-0678.
You Can Also Fill Out Our Contact Us Form Here to Talk with a Security Specialist – https://secureops.com/contact-us/







