The Use of Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Attacks and Cyber Defense
Artificial Intelligence or AI has ushered in a new era of technological advancement, with transformative effects in domains like healthcare and transportation. But perhaps nowhere is its impact more pronounced than in cybersecurity. As AI continues to evolve, it brings with it a new breed of cyber threats and defensive strategies, completely redefining the nature of this ongoing battle.
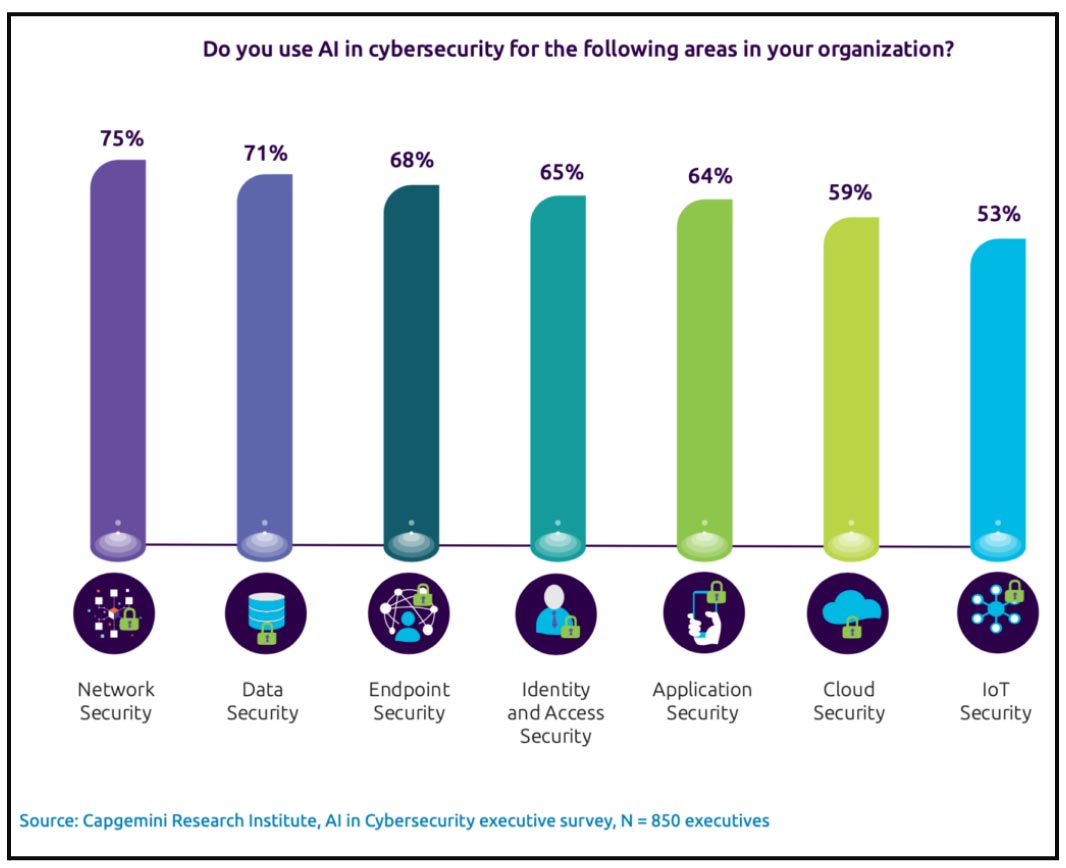
AI’s integration into cybersecurity is a natural progression of technology. Its ability to process large volumes of data and learn from patterns makes it the perfect tool for rapid threat detection and mitigation. What started as AI assisting in automating routine security tasks has now evolved into something much more.
AI-Powered Malware is Creating a New Generation of Attacks
Not only has AI become a powerful defense mechanism, but it has also given rise to a new generation of cyber threats. Attackers can now exploit AI’s capabilities to wreak havoc. Machine learning algorithms can be trained to find and exploit software vulnerabilities, enabling more precise and efficient attacks. Intrusion detection evasion, once the domain of skilled hackers, is now augmented by AI. Attackers can use AI algorithms to identify patterns in security systems and devise strategies to bypass them. Even AI-powered phishing attacks, capable of crafting convincing messages by analyzing communication patterns, pose significant challenges.
Example of an AI-Driven Attack – Using AI-powered bots for web scraping attacks.
The adoption of AI-powered bots for web scraping attacks introduces a paradigm shift in the capabilities of cybercriminals. These intelligent agents bring a slew of advantages that empower malicious actors in unprecedented ways. AI-driven bots can autonomously navigate through intricate website structures, swiftly adapting to changes and updates. Their ability to mimic human behavior grants them a cloak of invisibility, allowing them to blend seamlessly into legitimate traffic.
Moreover, these bots can execute scraping operations on a massive scale, extracting voluminous data at speeds that would be impossible through traditional methods. As cyber criminals harness the prowess of AI, the potential for targeted and efficient data extraction magnifies, posing significant challenges for organizations striving to protect their digital assets and user information.
As we were saying prior to the “scraping” attack example, the evolution of AI in cybersecurity has also sparked an arms race. Autonomous hacking systems, driven by AI, have emerged as a powerful weapon in this ongoing battle. These systems can autonomously identify targets, exploit vulnerabilities, and even adapt their strategies based on the target’s response. However, ethical concerns surround the use of AI in hacking systems, as they could be leveraged by governments, criminal organizations, and hacktivists for large-scale cyberattacks. Defensive strategies and international regulations must be re-evaluated to mitigate the risks posed by autonomous hacking.
AI is Providing Cyber Defense Better and More Efficient Tools
While AI empowers attackers, it also plays a crucial role in defensive strategies. Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify emerging threats and predict attack vectors, enabling organizations to strengthen their defenses before an attack occurs. Anomaly detection systems powered by AI can identify unusual patterns and trigger alerts for rapid response. Additionally, AI can automate the analysis of attack patterns, helping security teams identify the source and take countermeasures.
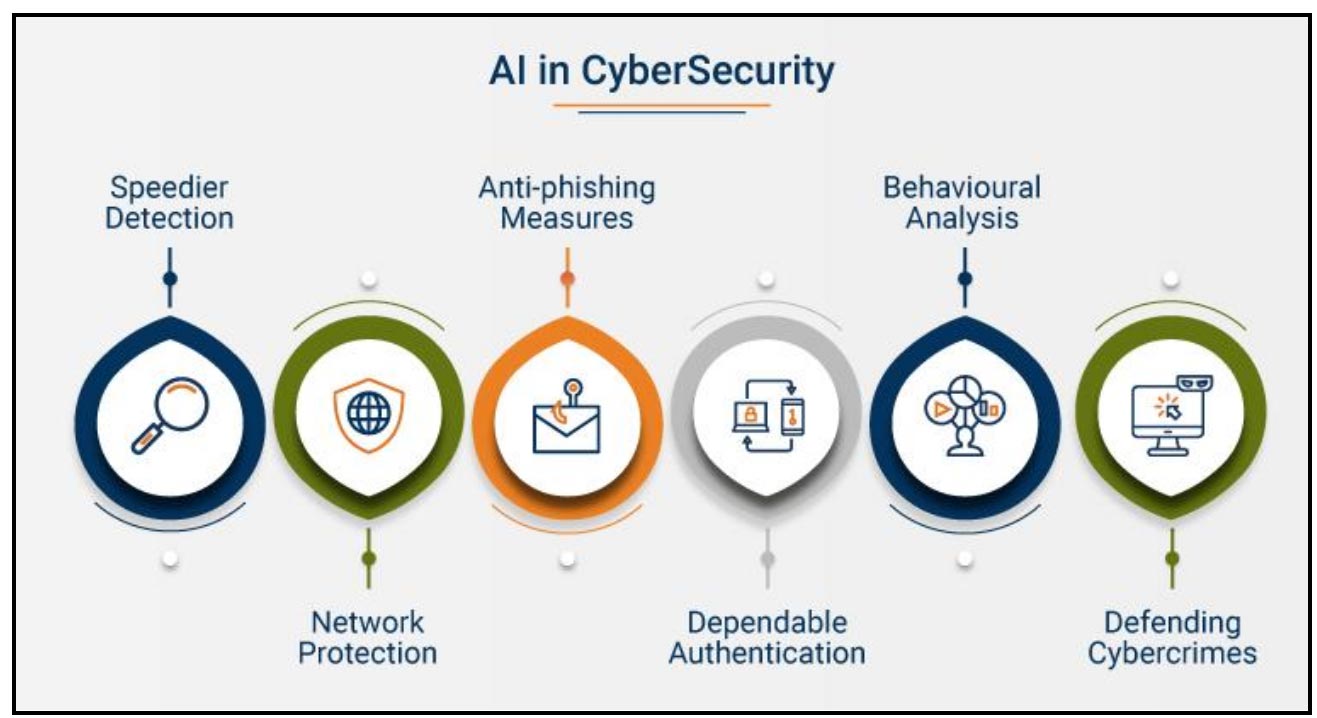
Figure 1 – How Will AI Help Organizations Uncover and Defend Cyberattacks
The Use of AI in Threat Hunting
Traditional security techniques, such as signatures or compromise indicators, are commonly employed to identify threats. While effective against known threats, these techniques may fall short when it comes to unknown threats. Signature-based methods can detect approximately 90% of threats, but integrating AI can boost detection rates to about 95%, albeit with an increase in false positives. To achieve optimal results, a combination of traditional methods and AI is recommended. This approach could deliver a 100% detection rate while minimizing false positives. Additionally, companies can leverage AI for enhanced threat hunting by incorporating behavioral analysis. For instance, AI models can be utilized to develop comprehensive profiles of each application within an organization’s network, leveraging large quantities of endpoint data.
The Use of AI in Vulnerability Management
Organizations face significant challenges in prioritizing and managing the multitude of new vulnerabilities they encounter on a daily basis. Instead of waiting for hackers to exploit high-risk vulnerabilities, traditional vulnerability management methods should be complemented with advanced techniques like User and Event Behavioral Analytics (UEBA). By analyzing baseline behavior of user accounts, endpoints, and servers, AI and machine learning can proactively detect anomalous behavior that may indicate a zero-day unknown attack. Implementing these measures can enhance organizations’ ability to protect themselves even before vulnerabilities are officially reported and patched.
The integration of AI into cybersecurity raises numerous ethical and legal quandaries. The use of AI in autonomous hacking systems challenges traditional concepts of human responsibility in cyberattacks. Identifying the responsible party becomes complex when the attack is orchestrated by AI, leading to the need for new legal frameworks and attribution methods. Furthermore, ethical considerations arise from the use of AI for offensive purposes. International agreements are crucial to establishing norms for the use of AI in cyber warfare, striking a balance between technological advancement and ethical responsibility.
Conclusion
Amidst all this, human analysts remain fundamental. AI may process data and identify patterns, but human intuition and expertise are necessary for contextual understanding and decision-making. Collaboration between AI and analysts creates a symbiotic relationship where AI accelerates data processing and threat identification while humans provide critical thinking and strategic insights. This partnership ensures a holistic approach, addressing cybersecurity threats’ technical and contextual aspects.
The evolution of AI in cybersecurity is an ongoing journey, with new frontiers yet to be explored. The potential is immense, but so are the ethical and legal challenges. As we continue on this path, it is crucial to anticipate and navigate these challenges to harness the full potential of AI while upholding ethical responsibility.






