What is Layered Security, including Phishing Defense?
As the rapidly changing cyber threat landscape continues to increase, so must our approaches to protecting against these threats. However, most organizations only realize they’re vulnerable after a breach has occurred.
Nearly 50% of the respondents reported having been victimized by a cyber-attack, including phishing attempts from malicious emails in the last year, and almost 30% were targeted by spear-phishing emails.
Protecting Yourself Against Phishing Attacks?
With increasing cyber-attacks by threat actors, SMBs, the elderly, and college students are now among the most common victims. These groups are often targeted because they’re easier to infiltrate than large organizations.
To stop these advanced phishing attacks, we recommend that organizations adopt a new approach focusing on technology and changing user behavior;
- Phishing attacks continue to increase because attackers can use them to bypass traditional email protection systems and send threats directly to their targets.
- Preventing various phishing attacks is often a blend between a technology solution and end-user education.
Advanced AI and Threat Intelligence Data Feeds can help reduce spam emails, trap phishing, BEC scams, and spear-phishing. Technical security layers cannot prevent all phishing attacks. Security awareness training can help the user community to learn how to identify hackers trying to steal their personal information.
What are the Various Phishing Attack methods?
Despite being one of its oldest tactics, phishing is an effective method for cybercriminals to gain access to organizations. However, even though these attacks continue to work today, most enterprise risk management (ERM) and cybersecurity solutions need to prioritize phishing detection and mitigation more.
 Phishers alter their various attack methods when targeting victims. Some of the most common phishing attacks include:
Phishers alter their various attack methods when targeting victims. Some of the most common phishing attacks include:
Email/Spam – Many people hate spam. To get rid of spam, you should know how to do it properly. You can block unwanted emails by configuring your mail server settings correctly. In addition, you can configure your mail client software so that it doesn’t automatically open every message.
Spear Phishing – A spear phishing email attacks a specific person or a group within an organization. Often this message will use impersonation attack methods. The hacker will scan social media channels for the target’s known contacts, including Facebook and LinkedIn. The hacker will craft an email as an impostor organization like Amazon, Microsoft, Apple and dozens more attempting to create a dialog with the victim.
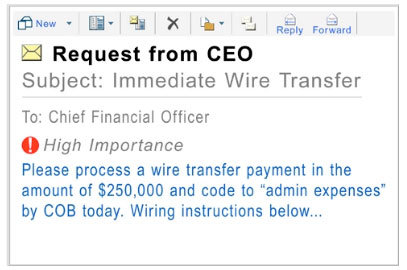
Whaling – Like spear phishing attacks, whaling phishing focuses on targeting specific organization leaders. The hacker will craft a message detailed to a CEO or, possibly, a CFO convincing the victim to provide financial information or access sensitive files.
Often a whaling attack is accomplished by the hacker attempting CEO fraud. The hacker will impersonate a CEO from another company while contacting the victim CEO. The FBI classified this type of attack as a business email compromise.
 Barrell Phishing–A variation of the classic phishing scam where an attacker sends out two identical messages, one to each recipient. They crafted one version to appear legitimate, while the second contains malicious code. When recipients open the second message, they unknowingly download malware onto their computers.
Barrell Phishing–A variation of the classic phishing scam where an attacker sends out two identical messages, one to each recipient. They crafted one version to appear legitimate, while the second contains malicious code. When recipients open the second message, they unknowingly download malware onto their computers.
Vishing – An increasingly challenging phishing method, vishing leverages voicemail to connect with the victim, often with either friendly or hostile messages. Vishing attacks often are challenging to prevent. Victims receive a voicemail from someone impersonating the IRS or claiming to be a long-lost friend. The victim will usually return the call left on the voicemail.
Smishing – Smishing attacks like vishing continue to affect many victims, including students, corporate users, and the elderly. As more people leverage SMS messaging, they will probably become a victim of smishing. A hacker will use an SMS message to lure the victim into a conversation. By establishing a level of rapport with the victim through texting, the hacker will make requests, including wire money to gain access to the victim’s bank account information, or their social security number. Smishing is challenging to prevent, and often only, end-user education is the only adaptive control.
 Trap Phishing– Trap Phishing emails rely heavily on their resemblance to legitimate messages. Therefore, people should be careful when inspecting traps Phishing – Trap Phishing email relies heavily on their similarity to genuine messages. Therefore, users should be cautious when checking links to avoid being lured into malicious sites. They should also examine grammar, spelling, and typographical errors. A trap phish would be everything from a fake CEO impersonation attack, an offer of employment, a message that you’ve won a million dollars, or something similar.
Trap Phishing– Trap Phishing emails rely heavily on their resemblance to legitimate messages. Therefore, people should be careful when inspecting traps Phishing – Trap Phishing email relies heavily on their similarity to genuine messages. Therefore, users should be cautious when checking links to avoid being lured into malicious sites. They should also examine grammar, spelling, and typographical errors. A trap phish would be everything from a fake CEO impersonation attack, an offer of employment, a message that you’ve won a million dollars, or something similar.
These scams blend in genuine content, such as the name of someone the user might recognize or a reference to a recent posting the user made on social media links to avoid falling victim to malicious websites. They should also check for grammatical mistakes, spelling mistakes, and typos. A trap phishing would be everything from a CEO impersonation attack to an offer of employment or a message that you have won a million dollars.
These attacks blend in legitimate content, including names of people the victim may know or a reference to a post the victim uploaded to Facebook.
Rise of Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing is a type of social engineering where attackers send emails pretending to come from trusted sources such as banks, online retailers, or government agencies. These messages often contain links to malicious sites that can infect your computer with viruses, spyware, or adware.
To protect yourself against phishing scams:
- Never open attachments sent from people you do not know
- Never click on a link to a website you don’t know or check the URL and make sure it will take you to a website that appears legitimate
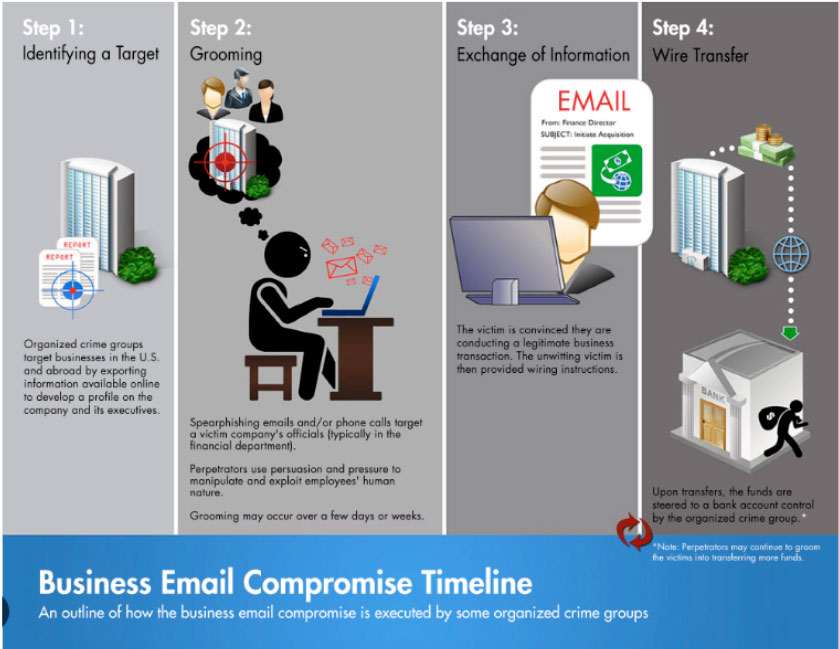
Email Phishing Defense Within the Layered Approach
Phishing threats, advanced email threats, and other attack vectors compel organizations to invest in a more advanced phishing defense strategy.
This layered concept provides multiple redundancies in the event systems and data are compromised. If one security layer is breached, defense-in-depth means that many more security layers will engage to increase the difficulty of a complete breach.
Layer-based cyber protection uses multiple methods to safeguard organizations from threats by deploying an adaptive security stack. It is like defense-in-depth in thickness, which operates many approaches to defend against attacks.
Defense in depth, layered security architecture:
- Physical controls – These controls include security measures that prevent physical access to IT systems, such as security guards or locked doors.
- Technical controls – Technical controls include security measures that protect network systems or resources using specialized hardware or software, such as a firewall appliance or antivirus program.
- Administrative controls – Administrative controls are security measures consisting of policies or procedures directed at an organization’s employees, e.g., instructing users to label sensitive information as “confidential”.
Email security solutions are one layer of a layered security solution. Email security is a term for describing different procedures and techniques for protecting email accounts, content, and communication against unauthorized access, loss, or compromise. Email is often used to successfully spread malware and spam. As we suggested, attackers use deceptive messages to entice recipients to part with sensitive information, open attachments or click on hyperlinks that install malware on the victim’s device. Email is also a common entry point for attackers looking to gain a foothold in an enterprise network and obtain valuable company data.
Enabling Multi-layer Security Approach to Threat Protection
Email security solutions in 2022 and 2023 continue to develop into the agile cloud platform.

The agile industry cloud platform contains several micro-services, including:
- Anti-spam, Anti-malware protection engines
- Adaptive artificial intelligence designed to process more security alerts along with enabling auto-remediation capabilities
- Data loss prevention and email encryption
- Multi-factor authentication capabilities with 2FA
- DMARC, SPF, and DKIM domain authentication protection layers
- Malicious URL detection and protection
Email security vendors continue to improve these technical controls to reduce phishing attacks. The email security industry’s platform approach with microservices to address a concern Gartner and SecOps have raised. Many depth-in-depth layers of defense strategies need more flexibility for organizations to enable adaptive security controls that fit their business model and attack risk posture. Email security companies responded by offering agile microservice capabilities for organizations to promote.
This strategy assists clients with both economic and operational concerns. By choosing specific micro-services, the organization can focus on controls that align with the business risk and only pay SaaS licensing costs based on their selected consumption.
If needed, the organization can enable more microservices within the existing management if the need arises.
The Role of an MSSP in Preventing Advanced Email Attacks
Organizations expecting an increase in email attack velocity will need more SecOps and NetSecOps resources. Often organizations struggle to gain access to global talent with experience in threat hunting, SecOps, DevOps, and risk management.
Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs) provides access to global talent through staff augmentation, 24 x 7 x 365 monitoring and incident response, and security deployment services. For clients choosing to leverage initial microservices offered by industry platform providers, understanding the human capital capacity, cost, and resource allocation commitment is critical to managing the organization’s layers of defense strategy.
- Many MSSPs often are specialists in specific security domains. Many offer services that includ managed firewalls, hosted identity management, and email security. Organizations planning to enable more email security microservices should consult an MSSP with the expertise and resources to support this strategy.
- MSSPs with email security experts have the needed experience to help organizations reduce the impact of email phishing attacks and data theft from insiders. These providers have expertise in email encryption for HIPAA, PCI, and other compliance mandates.
- MSSPs provides more significant security integration expertise if clients add additional adaptive controls to their security layers of defense strategy, including managing several adaptive controls.
- These providers help integrate email security, identity, zero-trust, and micro-segmentation by leveraging their security engineers with experience and expertise across these domains.
- The cost for any organization to hire and keep this experience and talent continues to take time and effort. MSSPs give organizations the needed resources, a 24 x7 coverage model, with a predictive cost model.
Conclusion
Preventing phishing takes a layer of defense approach against all email threat types. Here are some everyday reminders all users should remember when dealing with a suspected email, voicemail, or text.
These reminders include:
- Ensure the message has no misspelled words or is written with poor grammar.
- If personal calls you ask for financial information, hang up and call the number back. In most cases, the phone number will be disconnected or unavailable.
- If you receive a text message from a number you do not recognize, regardless of friendly the news is, delete the message. If this is a legitimate person trying to reach you, they will most likely call you.
- Check the sender’s email address if you receive a message from Amazon or FEDEX asking for account information to receive a package. If your email header address is not Amazon.com or FEDEX.Com, this is most likely a phishing email attempting a business email compromise.
- If you receive a phone call or email from the IRS, this is likely a trap phishing attack. The IRS does not use email or will not call you directly. The IRS continues to use regular postal mail to send out notices.
Layers of defense to adjust to the growing cybersecurity landscape requires organizational investment, leadership, and strategy. Addressing the velocity of email phishing attacks and constant changes in tactics used by hackers required an organization to be agile in its security strategies. Technology vendors offering platform services with service layer offerings for email security will give their customers only the needed tools. MSSPs play a critical role in partnering with organizations to help prevent phishing attacks affect their users.
We are here to help develop your layers of defense strategy. We have experience in email security and phishing attack prevention to help protect your organization’s data and users. Contact us via e-mail; we will happily walk you through a solution.
To Learn More About How to Secure Your Organization Please Call Us – as Always, We Are Happy to Help – 1 (888) 982-0678.
You Can Also Fill Out Our Contact Us Form to Talk with a Security Specialist – https://secureops.com/contact-us/







